In this article, we’ll learn about comparison between ARP vs RARP.
Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) and Reverse Address Resolution Protocol (RARP) are network protocols used for resolving layer 2 (Data Link Layer) addresses to layer 3 (Network Layer) addresses and vice versa.
ARP vs RARP: Network Protocols
| Feature | ARP (Address Resolution Protocol) | RARP (Reverse Address Resolution Protocol) |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Resolves a known IP address to a MAC address | Resolves a known MAC address to an IP address |
| Function | Maps an IP address to a corresponding MAC address | Maps a MAC address to a corresponding IP address |
| Operation | Broadcasts an ARP request to the entire local network | Broadcasts a RARP request to the entire local network |
| Protocol | Uses Ethernet frames in most cases | Uses Ethernet frames in most cases |
| Message Types | ARP Request, ARP Reply | RARP Request, RARP Reply |
| Address Type | Resolves logical (IP) addresses to physical (MAC) addresses | Resolves physical (MAC) addresses to logical (IP) addresses |
| Packet Structure | ARP packet includes sender and target IP and MAC addresses | RARP packet includes sender and target MAC addresses |
| Use Cases | Commonly used in Ethernet networks | Used in scenarios where diskless workstations need to discover their IP address |
| Broadcast vs. Unicast | ARP requests are broadcasted to all devices in the local network | RARP requests are broadcasted to all devices in the local network |
| Implementation | More widely implemented and used | Less common and mostly superseded by BOOTP and DHCP |
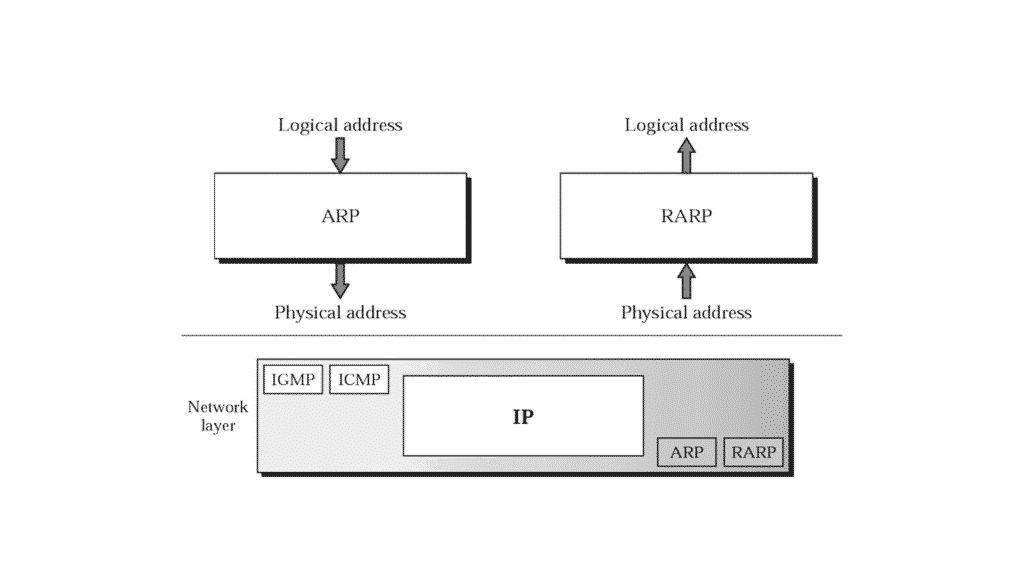
While ARP is still widely used, RARP has become less common and has been largely superseded by more modern protocols like BOOTP (Bootstrap Protocol) and DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) for IP address assignment in networks.
