Table of Contents
In this tutorial, you’ll learn about Phases of a Compiler, Analysis Phase, Synthesis Phase and more.
A compiler is a software program that converts the high-level source code written in a programming language into low-level machine code that can be executed by the computer hardware. The process of converting the source code into machine code involves several phases or stages, which are collectively known as the phases of a compiler.
Phases of a Compiler
There are two major phases of compilation, which in turn have many parts. Each of them takes input from the output of the previous level and works in a coordinated way.
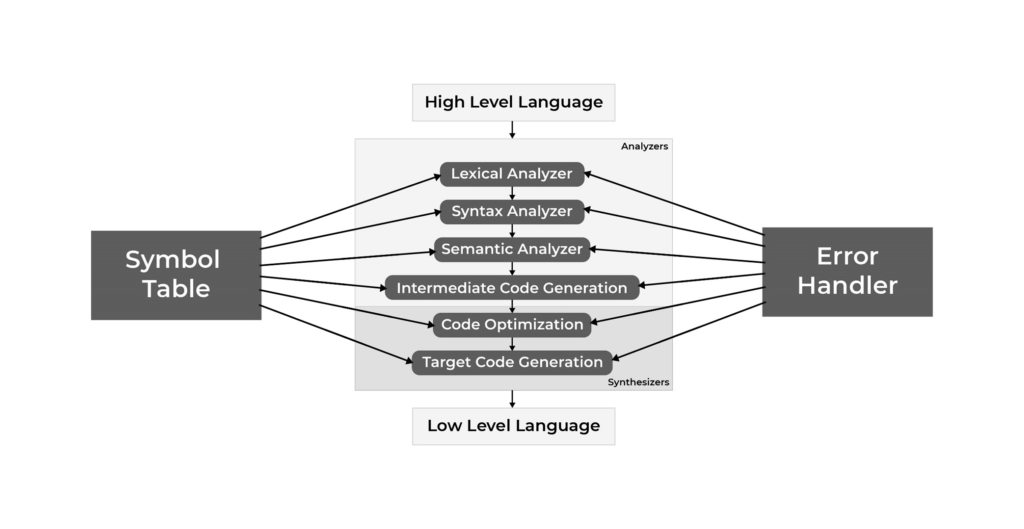
Analysis Phase
An intermediate representation is created from the given source code :
- Lexical Analyzer
- Syntax Analyzer
- Semantic Analyzer
- Intermediate Code Generator
The lexical analyzer divides the program into “tokens”, the Syntax analyzer recognizes “sentences” in the program using the syntax of the language and the Semantic analyzer checks the static semantics of each construct. Intermediate Code Generator generates “abstract” code.
Synthesis Phase
An equivalent target program is created from the intermediate representation. It has two parts :
- Code Optimizer
- Code Generator
Let’s Understand further sub-phases of Analysis Phase and Synthesis Phase of a compiler
Lexical Analysis
The first phase of a compiler is lexical analysis, also known as scanning. This phase reads the source code and breaks it into a stream of tokens, which are the basic units of the programming language. The tokens are then passed on to the next phase for further processing.
Syntax Analysis
The second phase of a compiler is syntax analysis, also known as parsing. This phase takes the stream of tokens generated by the lexical analysis phase and checks whether they conform to the grammar of the programming language. The output of this phase is usually an Abstract Syntax Tree (AST).
Semantic Analysis
The third phase of a compiler is semantic analysis. This phase checks whether the code is semantically correct, i.e., whether it conforms to the language’s type system and other semantic rules. In this stage, the compiler checks the meaning of the source code to ensure that it makes sense. The compiler performs type checking, which ensures that variables are used correctly and that operations are performed on compatible data types. The compiler also checks for other semantic errors, such as undeclared variables and incorrect function calls.
Intermediate Code Generation
The fourth phase of a compiler is intermediate code generation. This phase generates an intermediate representation of the source code that can be easily translated into machine code.
Optimization
The fifth phase of a compiler is optimization. This phase applies various optimization techniques to the intermediate code to improve the performance of the generated machine code.
Code Generation
The final phase of a compiler is code generation. This phase takes the optimized intermediate code and generates the actual machine code that can be executed by the target hardware.