Table of Contents
In this blog, we’ll learn about All Microsoft 365 Apps Explained and what is there purpose and why they are used.
In today’s fast-paced digital world, productivity is paramount. Whether you’re a student, a business professional, or simply someone who wants to get things done efficiently, Microsoft 365 is a must-have tool. This comprehensive suite of productivity applications offers a wide range of functionalities to help you create, collaborate, and manage your tasks effectively.
Microsoft Access

Microsoft Access is a database management system (DBMS) from Microsoft that combines the relational Access Database Engine (ACE) with a graphical user interface and software-development tools. It is a member of the Microsoft 365 suite of applications, included in the Professional and higher editions or sold separately.
Microsoft Access stores data in its own format based on the Access Database Engine (formerly Jet Database Engine). It can also import or link directly to data stored in other applications and databases.
Software developers, data architects and power users can use Microsoft Access to develop application software. Like other Microsoft Office applications, Access is supported by Visual Basic for Applications (VBA), an object-based programming language that can reference a variety of objects including the legacy DAO (Data Access Objects), ActiveX Data Objects, and many other ActiveX components. Visual objects used in forms and reports expose their methods and properties in the VBA programming environment, and VBA code modules may declare and call Windows operating system operations.
Microsoft Excel


Microsoft Excel is a spreadsheet editor developed by Microsoft for Windows, macOS, Android, iOS and iPadOS. It features calculation or computation capabilities, graphing tools, pivot tables, and a macro programming language called Visual Basic for Applications (VBA). Excel forms part of the Microsoft 365 suite of software.
Microsoft OneNote

Microsoft OneNote is note-taking software, developed by Microsoft. It is available as part of the Microsoft 365 suite and since 2014 has been free on all platforms outside the suite. OneNote is designed for free-form information gathering and multi-user collaboration. It gathers users’ notes, drawings, screen clippings, and audio commentaries. Notes can be shared with other OneNote users over the Internet or a network.
OneNote is also available as a free, stand-alone app via the official website and the app stores of: Windows 10, MacOS, iOS, iPadOS and Android. Microsoft also provides a web-based version of OneNote as part of OneDrive and Office for the web.
Microsoft Outlook

Microsoft Outlook is a personal information manager software system from Microsoft, available as a part of the Microsoft 365 software suites. Though primarily being popular as an email client for businesses, Outlook also includes functions such as calendaring, task managing, contact managing, note-taking, journal logging, web browsing, and RSS news aggregation.
Individuals can use Outlook as a stand-alone application; organizations can deploy it as multi-user software (through Microsoft Exchange Server or SharePoint) for shared functions such as mailboxes, calendars, folders, data aggregation (i.e., SharePoint lists), and as appointment scheduling apps.
Other than the paid software on Windows and Mac desktops that this article talks about, the Outlook name also covers several other current software:
- Outlook on the web, formerly Outlook Web App, a web version of Microsoft Outlook, included in Microsoft 365, Exchange Server, and Exchange Online (domain outlook.office365.com)
- Outlook for Windows, a new, free Outlook application that will be preloaded with Windows 11 from 2024
- Outlook Mobile, a mobile app version of Outlook
- Outlook.com, formerly Hotmail, a free personal email service offered by Microsoft alongside a webmail client (domain outlook.live.com)
Microsoft PowerPoint

Microsoft PowerPoint is a presentation program, created by Robert Gaskins and Dennis Austin at a software company named Forethought, Inc. It was released on April 20, 1987, initially for Macintosh computers only. Microsoft acquired PowerPoint for about $14 million three months after it appeared. This was Microsoft’s first significant acquisition, and Microsoft set up a new business unit for PowerPoint in Silicon Valley where Forethought had been located.
PowerPoint became a component of the Microsoft Office suite, first offered in 1989 for Macintosh and in 1990 for Windows, which bundled several Microsoft apps. Beginning with PowerPoint 4.0 (1994), PowerPoint was integrated into Microsoft Office development, and adopted shared common components and a converged user interface.
PowerPoint’s market share was very small at first, prior to introducing a version for Microsoft Windows, but grew rapidly with the growth of Windows and of Office. Since the late 1990s, PowerPoint’s worldwide market share of presentation software has been estimated at 95 percent.
PowerPoint was originally designed to provide visuals for group presentations within business organizations, but has come to be very widely used in many other communication situations, both in business and beyond. The impact of this much wider use of PowerPoint has been experienced as a powerful change throughout society, with strong reactions including advice that it should be used less, should be used differently, or should be used better.
The first PowerPoint version (Macintosh 1987) was used to produce overhead transparencies, the second (Macintosh 1988, Windows 1990) could also produce color 35 mm slides. The third version (Windows and Macintosh 1992) introduced video output of virtual slideshows to digital projectors, which would over time completely replace physical transparencies and slides. A dozen major versions since then have added many additional features and modes of operation and have made PowerPoint available beyond Apple Macintosh and Microsoft Windows, adding versions for iOS, Android, and web access.
SharePoint


SharePoint is a web-based collaborative platform that integrates natively with Microsoft 365. Launched in 2001, It allows organisations to create, manage, and share content and resources. It’s often used for building intranet portals, document management, and team collaboration spaces. The platform integrates with Microsoft Office and offers features like workflow automation, data storage, and business intelligence tools. With SharePoint Online, businesses can access company data, facilitating remote work and improving productivity. SharePoint was built for content management and team interaction and has integrated AI functionalities.
According to Microsoft, as of December 2020 SharePoint had over 200 million users.
Microsoft Power BI
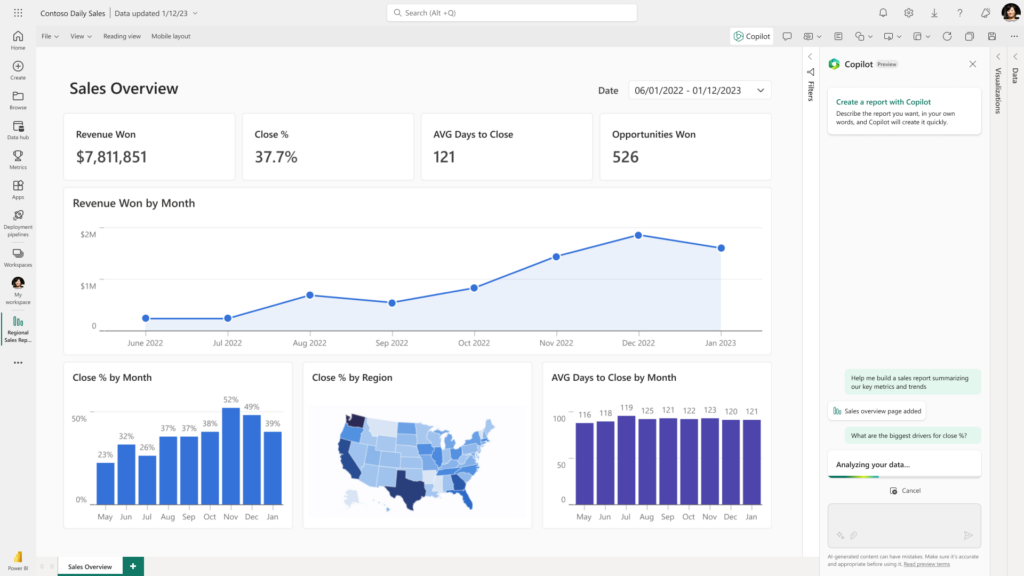

Microsoft Power BI is an interactive data visualization software product developed by Microsoft with a primary focus on business intelligence. It is part of the Microsoft Power Platform. Power BI is a collection of software services, apps, and connectors that work together to turn various sources of data into static and interactive data visualizations. Data may be input by reading directly from a database, webpage, PDF, or structured files such as spreadsheets, CSV, XML, JSON, XLSX, and SharePoint.
Microsoft Publisher


This is a desktop publishing software that enables you to create professional looking materials like letterheads, business cards, brochures, multi-column newsletters, multi-page manuals, calendars, labels, wide banners, oversized posters, greeting cards, and more. You can start off using a pre-designed template or a blank canvas to create your own design to match your corporate colors. It is a versatile and easy-to-use program and you do not need to be graphics designer to create stunning professional-looking documents with Microsoft Publisher.
Microsoft Teams


Microsoft Teams is a messaging app for organizations that provides a workspace for collaboration, communication, meetings, and file and app sharing. It’s part of the Microsoft 365 family of products and integrates with other Microsoft 365 apps like Planner and Power BI.
Microsoft Teams allows users to:
- Connect with communities for activities or work with teammates on projects
- Join audio and video calls in a secure setting
- Collaborate in documents
- Store files and photos with built-in cloud storage
- Create teams, which are groups of people who work together on projects, work, or common interests
- Create channels within teams, which can be standard channels available to everyone or private channels for focused conversations with a specific audience
- Use channels to hold meetings, have conversations, and work on files together
Microsoft Word

Word is a word processing application that has been around since 1983, making it one of Microsoft oldest application still in use today. Through the decades Microsoft continuously improved its interface, added features, and expanded its capabilities to make it one of the most popular applications for creating documents. It’s intuitive design makes it easy to use by almost anyone.
Create new documents from scratch or use one of the many pre-defined templates. Use Microsoft Word to create business letters, business cards, resumes, product manual, reports, flyers, restaurant menus, invitation cards, labels, forms, and many more. Features such as the ability to easily add a table of content, modify header and footer, track changes among your collaborators, add colorized data tables and charts, spell check your document, and a language translator make Microsoft Word a powerful tool to create a professional-looking document.
